How 5G Connectivity Will Boost The Output Volume of African Startups
5G is finally here. With the 5G infrastructure, it will become almost possible to download an HD movie in seven seconds — 40 times faster than 4G. This will be a big boost for countries like Equatorial Guinea where it will take over 22 hours to download a 5-gigabyte movie.

5G has now reached an advanced stage where it can be implemented on a wider scale after years of research. Countries like the US, the UK, South Korea, Japan, and the Scandinavian region are already positioning themselves for wide-scale adoption, first rolling out 5G services on a trial basis in select areas. For many, it would be fully operational by the end of 2019 or 2020. According to Ericsson, the new 5G technology has the business potential of $619 billion in revenue opportunity for telecom operators globally by 2026. Below, we consider how 5G technology will improve output volume of African startups.

Reduction in Cost
Among the potential advantages are high data rates, reduced latency, energy savings, cost reductions, and higher system capacity. Of course, you would expect an increase in cost by internet service providers for 5G services in order to cover the initial cost of installing 5G infrastructure, but all these would become inconsequential in the future as consumers can get more value for their services. The cost will include saving time and energy usage. A person with a 5G smartphone could download a 3-D movie in about 6 seconds. On 4G, it would take 6 minutes.
But note this: 5G is never really putting an end to the increasing cost of internet use. It is better to understand the implication of 5G technology from these contrasting sides of a coin. In 2013, you would require on average $76 a month for internet subscription according to the United States’ Bureau of Labor statistics. That figure is up 50% from the $51 a month consumers were paying in 2007, the year that the iPhone was launched. By 2019, Cisco (CSCO) forecasts that mobile data traffic to and from cell towers (not offloaded to Wi-Fi) will grow by 57%. With this forecast and should data plans stay the same four years down the road, the average user’s smartphone bill could grow by $43 a month to $119.
However, one key respite 5G is bringing to the table is in the quality of services.

In this regard, Emil Björnson of the Department of Electrical Engineering (ISY) Linköping University, Sweden notes that:
‘‘Initially, 5G subscriptions might cost more than 4G, so that the telecom operators can differentiate the different services. My guess is that with time the operators will push the monthly cost for a 5G subscription to the same range as today’s subscriptions, since most people don’t want to pay more than they are already doing. Hence you will get a much better service for your money. Huge investments will definitely be needed for 5G. Spectrum will be expensive, irrespective of what kind of bands that will be used. Deployment of new base stations and backhaul infrastructure will also be expensive.’’
So with faster internet infrastructure, expect more volumes of output.
The World Bank identified broadband Internet connectivity as a key catalyst for economic growth with every 10 percent increase in connectivity enabling a 1.38 percent growth in Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
“For instance, the average Internet speed in Nigeria might be 3.9Mbps but, if you are in Lagos, you could choose to buy a 4G connection and experience 10 to 20Mbps. If faster speeds are available, you do not need to worry about the average speed, hence it should not be a cause for slowing down economic activity. However, if you live or work in an area without fast access, then, for certain types of business, this would be an impediment to growth. Note also that if you do not have a fast access available your average speed is likely to be considerably worse than the nation’s average, because that’s the way averages work. This is the ‘Digital Divide’,” noted the Chief Executive Officer, Spectranet, David Venn.
5G Will Unleash More New Disruptive Ideas and Innovations
No gainsaying the fact that 5G technology will lead to the explosion of new disruptive ideas.
‘‘Many of the benefits probably aren’t yet apparent to us. Wireless network operators initially resisted proposals to give their customers mobile access to the internet, questioning why they would want it. At the dawn of 4G’s adoption no one could have predicted the new business models that grew on the back of mobile broadband, like Uber, Spotify and Facebook,’’ the World Economic Forum noted in its World Economic Forum Annual Meeting.

Unarguably, 5G would be a great enabler for the explosion of more disruptive innovations. One such innovation which has already achieved momentum is the Internet of Things. Embedded with electronics, Internet connectivity, and other forms of hardware, these devices can communicate and interact with others over the Internet, and they can be remotely monitored and controlled. One commentator describes how bizarre the world of the internet could get:
‘‘When someone wants Rebecca dead, he can just instruct her car to drive off a cliff. Mad stuff.’’
This is what ideas such as the Internet of Things are bringing to the table. One clear example of this is already seen in self-driving cars by Google. 5G will make such things become as ubiquitous as ever.
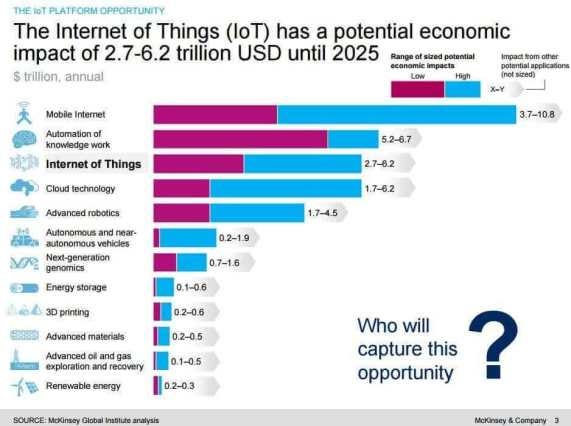
Consider alone the potential impact of the Internet of Things alone. McKinsey & Company says the Internet of Things (IoT) has a potential economic impact of $2.7 to $6.2T until 2025.
A host of disruptive applications will be built around 5G’s ultra-fast networks and real-time responsiveness once the infrastructure is fully deployed. Particularly, immediate disruptions are expected in these areas:
- massive Machine Type Communications (mMTC) such as solar-powered streetlights or other innovations to help citywide infrastructure
- Device-to-device public safety communications that don’t need active cellular coverage
- Real-time operations employing robotics to link surgeons with remote sites
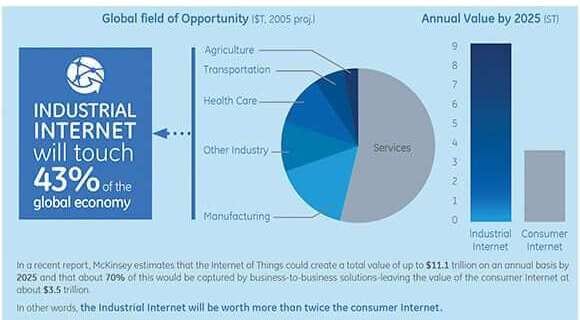
Machina Research forecasts “IoT will account for one-quarter of the global 41 million 5G connections in 2024.” Approximately ¾ of these will be in the auto industry via embedded vehicle connections.
Although the report sees 5G deployment “highly concentrated” in Japan, Korea, Europe, China and North America (with Japan and Korea leading the charge), it will also help operators extend their opportunities in new markets.
‘‘5G use case is in web apps. While it’s true that it’s just as easy to download apps as it is to download any program, and 5G makes the whole experience seem instant, you can free up storage space and avoid installation steps by using a web-based app that’s already set up and ready for you to stream from a web browser.
In other words, 5G will bring a world where you need very little storage on your phone because everything, including your apps, are instantly available from the cloud,’’ noted Tim Fisher, a technology expert
So get ready. 5G is bound to create more disruptions, just like Facebook, fin-techs and other digitally-focused platforms. For African startups, they would definitely be in the value chain.
See Also: Key Things Startups Should Know As The African Free Continental Free Trade Agreement ( AfCFTA ) Comes Into Operation July 7.
Upsurge In Internet Users. More Consumers Available Online
With 5G, expect a huge upsurge in the number of consumers available online. 5G will, therefore, provide network support for massive increases in data traffic. According to Cisco, by 2022, mobile will represent nearly 20 percent of all global IP traffic, fueled in part by the Internet of Things.
‘‘Mobile traffic will be on the verge of reaching an annual run rate of a zettabyte by the end of 2022. In that timeframe, mobile traffic will represent nearly 20 percent of global IP traffic and will reach 930 exabytes annually — nearly 113 times more than all mobile traffic generated globally in 2012. (An exabyte is 1,000,000,000 gigabytes and a zettabyte is 1,000 exabytes.),’’ noted Cisco in its annual Global Mobile Data Traffic Forecast Update (2017–2022)
5G will fuel more connectivity and internet penetration for consumers. Just take this fact for instance: although launched in 2014, in 2017, 4G already carried 72 percent of the total mobile traffic and represented the largest share of mobile data traffic by network type.
Cisco predicts that 4G will continue to grow faster than other networks, however, the percentage share will go down slightly to 71 percent of all mobile data traffic by 2022.
“The full value and transformational capabilities of 5G cannot simply be measured by performance improvements over 4G (higher bandwidth, broader coverage, and lower latency),” wrote Thomas Barnett, director of Cisco’s service-provider thought leadership in a blog about the report. “5G will also deliver enhanced power efficiency, cost optimization, massive IoT connection density and dynamic allocation of resources based on awareness of content, user, and location.”

Cisco’s study also noted that 5G growth will be driven by IoT applications — sensors and meters on the low end to autonomous cars on the high end. Awareness of content, user and location will determine how 5G resources are allocated. “This technology is expected to solve frequency licensing and spectrum management issues. Large scale commercial deployments are not expected until the latter years of the current forecast.

Interestingly, Cisco’s forecast also sees an opportunity for internet-based businesses, as more and more consumers will find online presence almost inescapable.
The study notes that:
- By 2022, 5G connections will represent over three percent of total mobile connections and will account for nearly 12 percent of global mobile data traffic.
- By 2022, the average 5G connection (22 GB/month) will generate nearly three times more traffic than the average 4G connection (8 GB/month).
- By 2022, 4G connections will be 54.3 percent of total mobile connections, compared to 34.7 percent in 2017. The global mobile 4G connections will grow from 3 billion in 2017 to 6.7 billion by 2022 at a CAGR of 18 percent. 5G connections will appear on the scene in 2019 and will grow several thousand percents from under half a million in 2019 to over 400 million by 2022.
Indeed, 5G will create a whole new world of customer experience.
5G will also change Peer-to-Peer connections because instead of just servers having access to quick upload speeds, your phone and computer can do the same.
‘‘Every 5G cell has a minimum upload speed of 10 Gbps (1.25 gigabytes per second), meaning that in ideal conditions, users can transfer 1.25 GB of data every single second between devices. This is much faster than what’s currently widely available. Having such a fast upload speed on your end, and other people having access to 5G’s ultrafast download speeds, means that others can download data from you as fast as you can upload it,’’ Fisher noted.
‘‘P2P can be used in many forms, like when making phone calls, transferring files, relaying information between vehicles in a smart city, automating factory equipment, and interconnecting smart sensors in homes, cities, farms, etc.’’
Bottom Line
5G will definitely see a boom in the African startup ecosystem. It will not only make the mobile experience efficient but memorable. World Bank report estimates show that a 10% higher 3G penetration in 2012 resulted in an increase of 0.15 percentage points in the annual growth rate of GDP per capita. The study also estimated the impact of mobile data usage across 14 countries found that a doubling of mobile data consumption raised GDP by 0.5 percentage points. The study also noted that for every 10 percentage point increase in broadband penetration in China there was a 2.14% increase in GDP.

In contrast to other findings that broadband has the biggest economic impact of all ICTs, simple 2G mobile penetration was found to have a bigger and more significant impact than fixed broadband on the Senegalese economy. Each 10 percentage point increase in mobile penetration was found to raise GDP growth by 0.44% (at a 10% significance level).
So African startups should expect more from 5G! Such sectors that would see the immediate impact are Virtual and augmented reality, video, and music streaming services, among others.
Charles Rapulu Udoh

Charles Rapulu Udoh is a Lagos-based Lawyer with special focus on Business Law, Intellectual Property Rights, Entertainment and Technology Law. He is also an award-winning writer. Working for notable organizations so far has exposed him to some of industry best practices in business, finance strategies, law, dispute resolution, and data analytics both in Nigeria and across the world.




