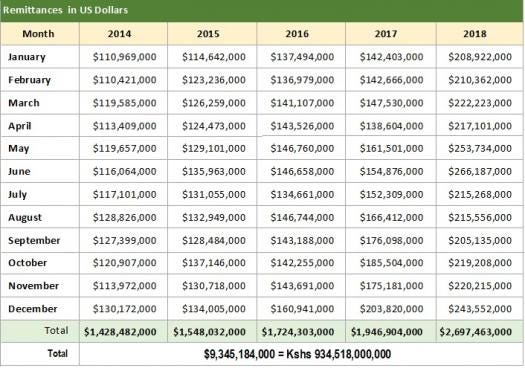
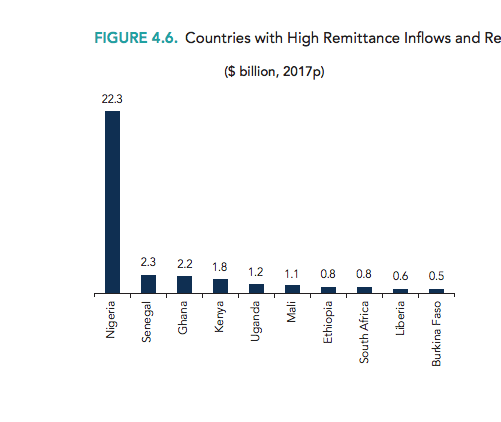
Kenyan Recruitment Startup Lynk Raises Funding For Expansion
Kenyan recruitment startup, Lynk is the newest to join the train of startup fund-raising in Africa. Though the amount raised is undisclosed, it is larger than Lynk’s combined total of previous funding, which was a US$1.3 million seed round and US$500,000 in grant money.

A Look At The Funding
- This round of funding was led by Lateral Capital and featured local and international family offices and funds such as the Cornerstone Group.
- Lynk co-founder Johannes Degn said the funding would be used to help the startup expand its operational footprint, grow its team and improve its B2B offering.
“It will almost exclusively be for salaries as we are hiring a more senior team. We are growing our commercial presence in Nairobi. Our ability to grow market size in Nairobi is the remaining proof point before expanding to second market. We have budgeted a good amount for marketing activities,” Degn said.
What The Startup Does
Lynk connects informal artisans with customers. It allows customers to book professional services from highly vetted artisans. Customers can simply book an assessment with the artisan and the artisans will be with them in as quickly as 4 hours. Quotes are provided at set rates, and assessment costs are deducted from the total job value. So whether it is a gentle full body Swedish massage for deep relaxation or the installation and replacement of sinks, baths, showers, and toilets, Lynk is up for it.
The Kenyan startup also says there is no way a wrong artisan would turn up.
‘‘We’ve been connecting customers to workers since 2015. Our customer base trusts and believes in the quality of our services and our digital platform always the entire process to be transparent — you don’t need to work about inexperienced workers, hassle about payments or rates, or worry about communication. We serve as the neutral intermediary and ensure all work is delivered and completed to industry standards. This means ensuring that the Pros we connect you with have a breadth of experience, are professional, trained, and certified in their craft. Once we find the right match, we will notify you of the details — name, and contacts of your Pro before the service,’’ it notes.
The startup was started in 2015.
So far, the Lynk platform claims it has facilitated more than 31,000 jobs and over 100 construction projects.
Charles Rapulu Udoh

Charles Rapulu Udoh is a Lagos-based Lawyer with special focus on Business Law, Intellectual Property Rights, Entertainment and Technology Law. He is also an award-winning writer. Working for notable organizations so far has exposed him to some of industry best practices in business, finance strategies, law, dispute resolution, and data analytics both in Nigeria and across the world.