How Sairui, The African New Retail Option Would Disrupt E-commerce In Africa
Nothing lasts forever, goes the saying. For the Baby Boomers and Generation X who existed without the internet, it was a shock that the traditional, physical retail business model could fade away, to be replaced by the business at the click of a button.
Today, Amazon Effect means that traditional, physical retail shops continue to wind down and call it a quit, giving in to the stiff competition from Amazon, eBay, Alibaba, Jumia and online shops. For emerging markets and developing countries, what remains for these physical shops to be completely rendered to ruins is trust.
With massive trust and pervasive internet connectivity in developing economies such as Africa’s, physical shops may soon be bidding their last farewell. In fact, Statista predicts that e-commerce penetration will grow from 9% in 2017 to 12.4% by 2020.
But here is the caveat: internet commerce itself is not safe.

Chinese billionaire, Jack Ma, understood this early enough. In 2016, Jack Ma started a revolution he called the ‘New Retail’ that would itself redefine what commerce really means for all of us. Jack Ma is the 21st richest man in the world and the number one richest man in the most populous nation on Earth— China.
He is piercing the heart of commerce and extracting what has fueled commerce over the course of thousands of years ago — human beings. Through new retail trade, he is relaunching the whole idea of technology in commerce and trade itself to the people that originally own them — human beings, consumers.
“Commerce as we know it is changing in front of our eyes. E-commerce” is rapidly evolving into “New Retail.” ,” Ma wrote to Alibaba shareholders in a letter sent ahead of the New York-listed company’s annual shareholders in 2016. ”The boundary between offline and online commerce disappears as we focus on fulfilling the personalized needs of each customer. We anticipate the birth of a re-imagined retail industry driven by the integration of online, offline, logistics and data across a single value chain. This is why we are adapting, and it’s why we strive to play a major role in the advancement of this new economic environment.”
This may sound more Utopian than realistic, but in China where the concept was formed, Hema Supermarket, an arm of Alibaba that specializes in new retail, has opened 64 Hema stores in 14 cities, with over 10 million customers shopping at these supermarkets since the beginning of 2016.
On average, for a Hema Supermarket that has been open for at least 1.5 years, daily average sales are upwards of 800,000 yuan (US$116,500) — about 60 percent of which comes from online orders. Based on Alibaba’s data, offering a combination of online and offline shopping options results in an increase in average monthly spending by customers. Consumers who shopped both online and offline at Hema spent an average of 575 yuan monthly, compared to under 300 yuan for purely online, or purely offline shoppers.
See Post: Airtel Africa Initiates IPO On The London Stock Exchange, Public Trading Still July 4
Pinduoduo, the $1.5B Chinese startup is also another Chinese e-commerce company, engaged in new retail. The startup is challenging the giant Alibaba in China’s towns and villages. In January, Pinduoduo had 114 million active users, surpassing that of New York-listed Chinese discount retailer Vipshop. Currently, the startup has captured a projected 7.0% of all retail e-commerce sales in China this year, not a bad showing for a firm that launched in 2015. In three short years, Pinduoduo has emerged as one of China’s fastest growing shopping startups, with as many as 55 million users accessing the site per day.
Pinduoduo’s idea of new retail comes by way of offering group discounts.
Here Is How The Idea of New Retail Works
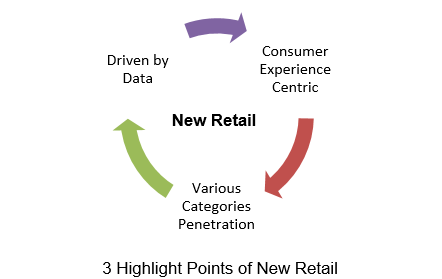
The idea of new retail lies in thinking beyond the boundaries of the two-party system of retail operations, that is, e-commerce and legacy brick-and-mortar retailing. New retail, instead, focuses on employing an entirely new operating system for reaching and inspiring consumers to shop.
‘‘New Retail trade is trying to solve two particular core challenges in the industry,’’ Emmanuel Elem, an advocate of Sairui, Africa’s new retail startup said. ‘‘The first challenge is the challenge of cold war between offline and online malls. Shoprite is an offline multi-billion dollar shopping mall, for example. On the other hand, Jumia is an online mall. These two different malls are doing things differently and the truth is that they are struggling for the same customers.’’
Now, there are people who have sworn [or who are so internet phobic] that they cannot buy or make payment on the internet because they cannot see the person they are buying from. There are also people that say they don’t have the time to go to Shoprite and begin to buy things [be in the queue and waste their time?] when they have Jumia that can get them what they want in their houses while they wait patiently for delivery to be made. So what new retail is trying to do is to bring a marriage between online malls and offline malls.
By new retail, it will no longer be about online shopping malls.
They will also have offline shopping malls or offline distribution centers where people can go, select what they want, pay online and if they don’t want to pay online, they can go to the mall offline and make payment and collect the goods, with the coupon they present to the owner of the shop.’’
He says new retail trade represents a system that blends the best of what both offline and online worlds have to offer. Apart from that, it also offers the best of an entirely new mix of human, digital and physical experience design, giving consumers a new means of inspiration, selection, immediate gratification, physical sensation and convenience, and that ultimately renders the distinction of digital vs. physical irrelevant.
Sairui, The First African New Retail Option Is Gaining Momentum
Although launched this year, March, Sairui is on course to change the idea of internet retail trade. Modeled after Chinese Pindoudou, the startup, which has its Africa headquarters in Accra, Ghana sells everything from clothing to hardware and other commodities and offers large discounts to purchasers. The startup has a strong presence in Nigeria and is also extending to other Africa countries like Cameroon, Uganda, Zambia, Tanzania, and other places.
‘‘We are doing this simultaneously,’’ said Elem. ‘‘Sairui is all about supporting grassroots entrepreneurship. Sairui shows people the possibility of starting to build a business no matter how small they have because with as small as less than 10,000 naira, they can become a business build through Sairui. This is exactly what it’s called pure grassroots entrepreneurship. Sairui also has bigger packages for those that don’t want to start with such small amounts of money.’’
The startup says it has multiple certified safeguard mechanisms, genuine licensed goods at lower prices and more reliable quality.
The Major Changes The Startup Is Bringing To The Table Are In The Logistics And The Customer Experience Areas
The startup offers large discounts to its online shoppers, bringing on-board an entirely new way of buying and selling.
‘‘What Sairui has brought in is the possibility of online and offline shoppers becoming business owners while also shopping. This has nothing to do with network marketing,’’ Elem said. ‘‘Network marketing is a different ball game altogether. Sairui has variety of products.’’
Elem said to handle logistics, the startup has physical shops where the online shoppers can go, present their coupons and redeem their goods or simply make new purchases.
‘‘Sairui is not opening up physical shops on its own. Sairui is opening up these physical shop through partnership or mini-franchising. These shops are called service centers. The centers are there to service our customers who can come and pick up these products. It is either you pay the company online or through these service centers. You can select your products online or you go to the service centers, give them your cash and carry your products. But the simple truth is that the products are going to be very affordable.Right now, we have about three physical malls in Nigeria through what we call Service centers. We service our customers through our customers centers there. We have centers in Cameroun. We have in South Africa. Right now, we have in about seven African countries.’’

For a startup that is just three months old, this appears a great streak of success, but the startup believes its incorporation of Jack Ma’s concept of new retail trade into its business strategy doesn’t just stop at setting up physical locations to enhance internet commerce experience but also that the strategy means consumers on the platform would get a chance to develop business interests from their purchasing or consumption needs.
‘‘Sairui is not a B2B company. Sairui deals directly with end users. We are dealing directly with the end users; people that are consuming these products. We are not dealing with business owners . We are making the end users business owners and also consumers linking them up directly with the manufacturers of these products, removing the middle person involved,’’ Mr. Elem said.
But it does appear that even the B2B middlemen would still have a say after all since the aim is to turn your consumption cost into instant profitability.
‘‘If you do some shopping on a $100 product on Sairui, for instance, we are giving you a discount of 60% on each product, meaning you’re getting a chance to buy two more products. Now, Sairui will help you sell those two discounted products you bought through its wholesale store,online or offline, free of charge. Sairui will sell each of them on your behalf at $100 each, the initial retail price at which you bought them.’’

The startup boasts it would sell off the products on behalf of its customers within a 7 to 10 days period, leaving customers with some unexpected side profit, long hours after they have made their first purchases.
‘‘We are the pioneer of this kind of system,” Elem said. ‘‘It may be strange to African markets, but the simple truth is that over 20,000 e-commerce companies are already using new retail to run their businesses in China. You can trade as many times as you want with one-time principal.’’

Elem said offering discount does not represent any loss for the startup because of a direct partnership with manufacturers of the goods sold by the startup. He said Sairui mall is an open market place just like Amazon, and as such, anything is bound to happen.
‘‘It is just like asking people why they drink water from a clean cup,’’ he said. ‘‘Nobody would see what is good and wouldn’t want to go for it. The general ideology of new retail is encouraging grassroots entrepreneurship. Sairui is a unique opportunity that anyone shouldn’t miss, even though not for the sake of profit, but for the sake of buying things affordable prices and getting free products from its online or offline shops.’’
Getting Started With Sairuimall Africa
To learn more about how to be part of the Sairui value chain, contact the startup’s country director on +2348039421770
Charles Rapulu Udoh

Charles Rapulu Udoh is a Lagos-based Lawyer with special focus on Business Law, Intellectual Property Rights, Entertainment and Technology Law. He is also an award-winning writer. Working for notable organizations so far has exposed him to some of industry best practices in business, finance strategies, law, dispute resolution, and data analytics both in Nigeria and across the world.