Expect more cars, or more ride-hailing options soon across major African cities. Russian startup inDriver is next on the line. Already launched in Arusha, Tanzania last year, inDriver has expanded to Nairobi, Johannesburg and Cape Town. Its next bus stop is most likely Nigeria, and that would be sooner than you think. The startup’s aim is to enter major cities in Nigeria, Kenya, Ghana, Zimbabwe, Uganda, and Namibia within the shortest feasible time. It has recently been subtly pushing for drivers to register with it in Nigeria.
Here Is Why inDriver May Put Up A Fight With Uber Or Bolt For Market Shares
At A Glance:
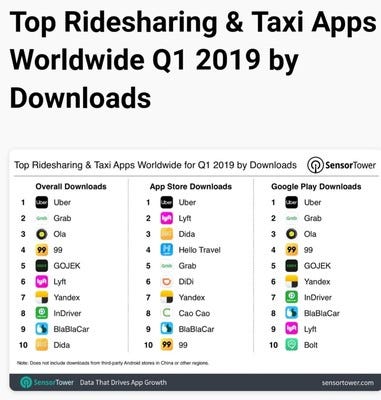
- Founded in Yakutsk in 2012, inDriver now has more than 24 million users in more than 200 cities in over 20 countries.
- The startup is one of the top 10 ridesharing and taxi apps worldwide by downloads.
- Currently, the company operates in the United States, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Armenia, Brazil, Mexico, Guatemala, Colombia, Peru, El Salvador, Chile, Ecuador, Costa Rica, Panama, Honduras, Dominican Republic, Bolivia, Tanzania, South Africa and Kenya.
- In fact, in just six months after launch, more than 60 thousand people joined the startup either as drivers or riders.
Johannesburg:
In Johannesburg, South Africa, inDriver already has an estimated 3,000 registered drivers.
Creativity In Competition:
inDriver’s strategy is to give its customers the power to fix the fare they would want to pay, much like traditional car-hailing taxis, except, of course, that the customers, instead of the drivers, peg the initial offer.
“Passengers enter the amount they are willing to pay for a trip and drivers then bid on the offer. The bargaining function on the app makes the ride-hailing service well suited to longer commutes, from neighbouring suburbs into hubs like Sandton and the CBD.
“A unique feature to inDriver is that drivers are not automatically assigned to riders. Passengers receive multiple offers from drivers in the area and are given the opportunity to select one based on fare amounts, driver ratings, estimated time of arrival and vehicle model. The trip is confirmed once both parties agree to the fare,” the startup said.
This innovation is probably a game changer in the face of growing stiff competition with the other car-hailing startups such as Uber and Taxify, and the depreciating purchasing power of car-hailing users in Africa.
However, unlike others that allow you to pay using your credit cards, inDriver says it works on a cash-only basis.
Safety:
inDriver has security features such as “A safety button’’ for both driver and rider, linked to emergency numbers, and is integrated into the app. In addition, both parties can share their GPS location and other details of rides in real time with trusted contacts.
Drivers Are Increasingly Having A Say In The Multi-Billion Dollar Industry.
The first problem inDriver is planning to solve to stick out of the competition is to endear itself to its drivers. Thus, even if the hailers have cut their prices, the drivers always have the final say, by way of the commission they earn. There are already signs that the startup has its drivers at heart.
What it did in Tanzania was a big shot. Drivers were given an initial six-month period without charging commissions after which the startup charged the drivers just 5% to 8% in commissions. At this rate, it is the lowest by commission among the three major car-hailing companies. Uber is charging 25% and Bolt is hovering around 15%. In addition to the attractive commissions, drivers will also be able to view both pick-up and destination points before accepting rides.

The competition would, of course, be fierce. Drivers who are willing to work long hours may win, not riders. This is because each driver can now sign up on all the competing platforms and become more loyal to the ones that respect their time and hard work, at the same time honoring riders by giving them more reasons to hail them.
Does this mean more income for the ride-hailing industries yet? Not very much in the offing. Each of them would have to contend with operational cost and the need to make profit and scale to the business. But the problem still remains that winning drivers’ loyalty only by doling out incentives will most possibly mean subsidizing customer rides for a longer time, and more promotions, of course, to boost drivers’ earnings.
In all these, the startups may keep losing, failing to even record a profitable outing. Ask Uber which just filed its SEC-1 and completed its IPO recently. The company’s largest expense in the middle of huge losses on a global scale is its “cost of revenue.” The cost of revenue is a category that includes incentives paid to drivers.

The news may be more pessimistic than it is cheerful, but here is the fact: over the past seven months, inDriver, a five-year-old Russian ride-hailing company, has gone from launching in its first African city to operating in four. It does seem something has finally come home to roost.
And gradually, global ride-hailing giant Uber has gone from having no competitors in Africa to having more than 50.
Charles Rapulu Udoh

Charles Rapulu Udoh is a Lagos-based Lawyer with special focus on Business Law, Intellectual Property Rights, Entertainment and Technology Law. He is also an award-winning writer. Working for notable organizations so far has exposed him to some of industry best practices in business, finance strategies, law, dispute resolution, and data analytics both in Nigeria and across the world.
